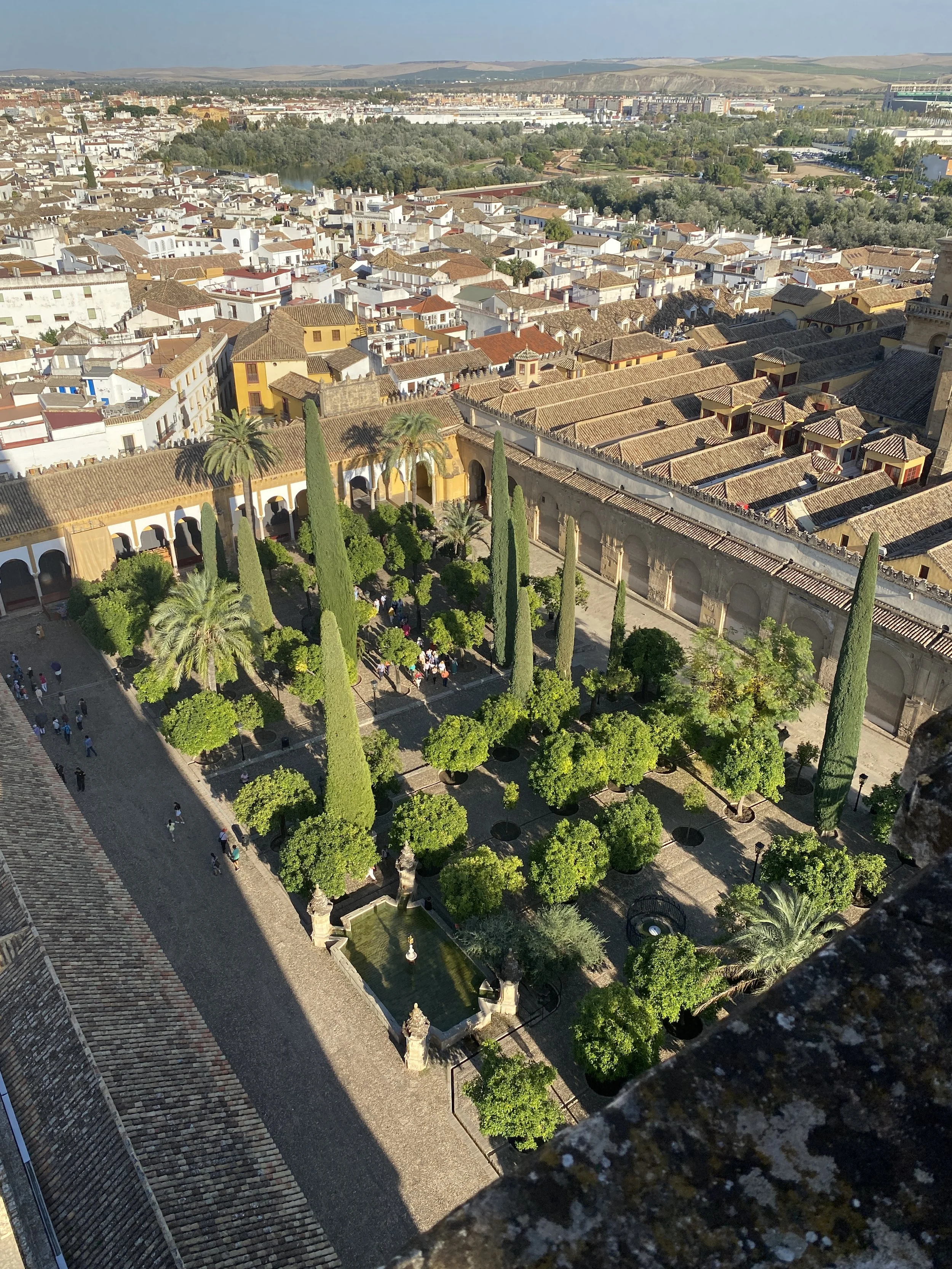
Explore one of the largest amphitheaters (as seen on Game of Thrones!) and admire the impressive mosaics on a day trip from Seville to the ruins of the first Ancient Roman town outside of Italy.
The House of the Birds is the largest complex at Itálica.
Since Wally and I were spending five days in Sevilla, Spain, we figured we could add the nearby Roman ruins of Itálica to our itinerary. It reminded us of visiting the ruins of Volubilis outside of the city of Meknès, Morocco (although the Spanish weather was much nicer). We both share a passion for history: Wally’s childhood interest in Ancient Rome matches my fascination with Ancient Egypt (which we were fortunate enough to experience together, but I digress).
“The amphitheater was used as a filming location for ‘Game of Thrones.’
Thanks to some CGI magic, it served as the Dragonpit.”
The Venus of Itálica was unearthed in 1940. This is a replica — the actual statue is in the Archaeological Museum of Seville.
The archaeological park of Itálica (which Wally joking referred to as Italics) is located about 30 minutes northwest of Sevilla, in the municipality of Santiponce, and is one of the cultural points of interest along the Ruta Bética Romana, the Roman Baetica Route — an ancient Roman road that runs through the provinces of Sevilla, Cádiz and Córdoba. If you’re so inclined, you can walk it, though it’ll take you weeks.
We had already done our fair share of walking, and since it was unseasonably hot, opted to take the 170A bus from the Plaza de Armas station, which typically departs every half hour from Sevilla.
A replica of the 2nd century statue of Diana, goddess of the hunt, greets visitors to Itálica.
Roman Expansion: A Brief History of Itálica
Itálica was the first Roman city established outside of Italy and thrived from the 2nd to the 4th century CE. Its origins can be traced back to General Scipio Africanus’ victory at Ilipa (near Sevilla) in 206 CE. During the Second Punic War, Scipio’s tactical efforts against Hannibal and the Carthaginians focused on the lower Guadalquivir valley, and after conquering the region, he established the settlement for his veteran troops to live.
Itálica bore witness to the births of Trajan (53-117 CE) and his adopted son and successor, Hadrian (76-138 CE) who were the first Roman emperors born outside of Italy.
A reproduction of a statue of the Roman emperor Trajan in heroic pose found in Itálica. The original can be seen at the — you guessed it — Archaeological Museum of Seville.
Hadrian expanded the city to include the Urbs Nova, literally the “New City,” added an impressive amphitheater and elevated its status to colonia—the highest designation for a Roman city. Additionally, Itálica amassed significant wealth from the exportation of grain and olive oil grown in the fertile soil of the Gerena Depression. These goods were transported to the Guadalquivir River and shipped to Rome by boat.
However, by the 4th century, the combined impact of mass deforestation and poor agricultural practices left Itálica’s river port dry, ultimately causing the city to be abandoned.
Aside from a group of schoolchildren, we pretty much had Itálica to ourselves.
Visiting Itálica
After a short walk from the bus stop, Wally and I arrived at the park entrance. We purchased the very affordable admission: 3€ ($3.25) for both of us. It’s free for EU citizens. Bring some cash — they don’t take credit cards.
Plaques and a milestone with Hadrian’s name on it
We made a detour to the restroom, which is located in a nearby building, where we saw a commemorative plaque bearing the names of individuals who financed the early excavations at Itálica, as well as a marble milestone inscribed with Emperor Hadrian’s name.
I wasn’t sure what to expect. Most exposed ruins, those not buried beneath sand or soil, were commonly pillaged and used as a source of building materials by whomever occupied the region after they had been abandoned. Additional bits were plundered during the French occupation of Spain, and in the 18th century, a mosaic called the Loves of Zeus was taken by Regla Manjón, the Countess of Lebrija, and incorporated into her palatial home in Sevilla. Several artifacts, including the erotic Abduction of Hylas, are displayed at the Museo Arqueológico de Sevilla (the Archeological Museum of Seville).
In 1912, the complex was officially declared a national monument, ensuring its conservation and protection against further looting.
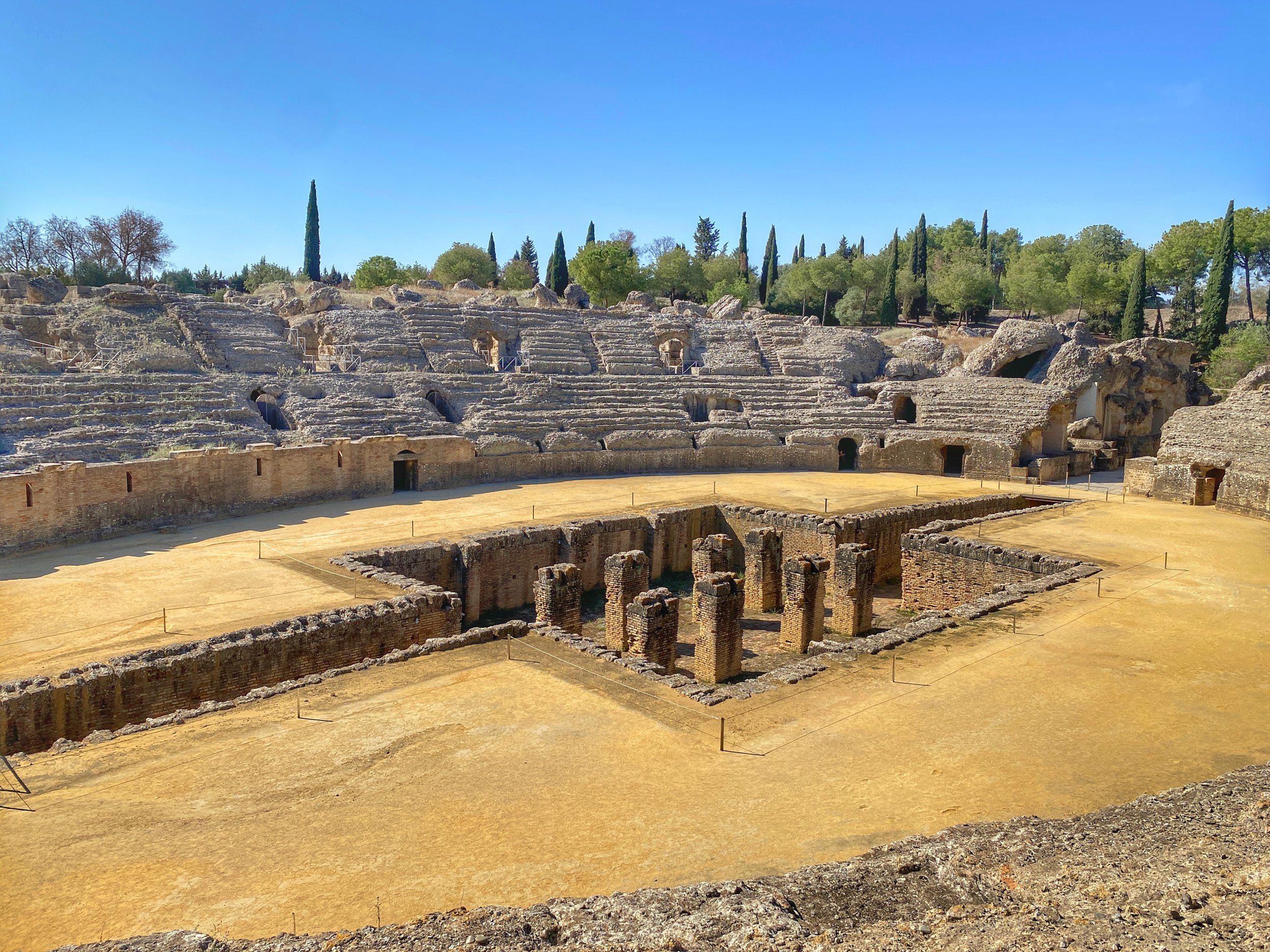
Start your visit to Itálica by exploring the amphitheater.
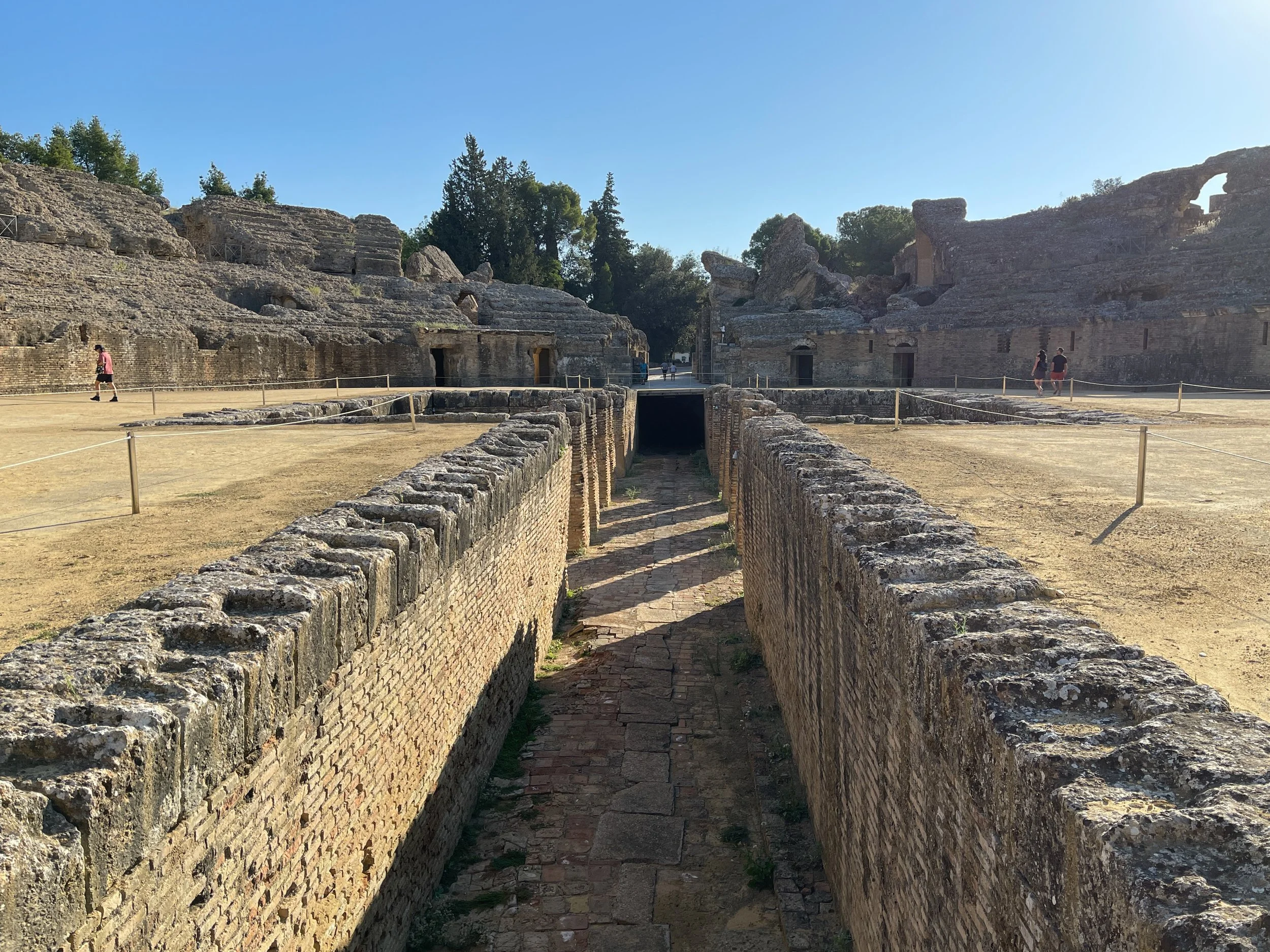
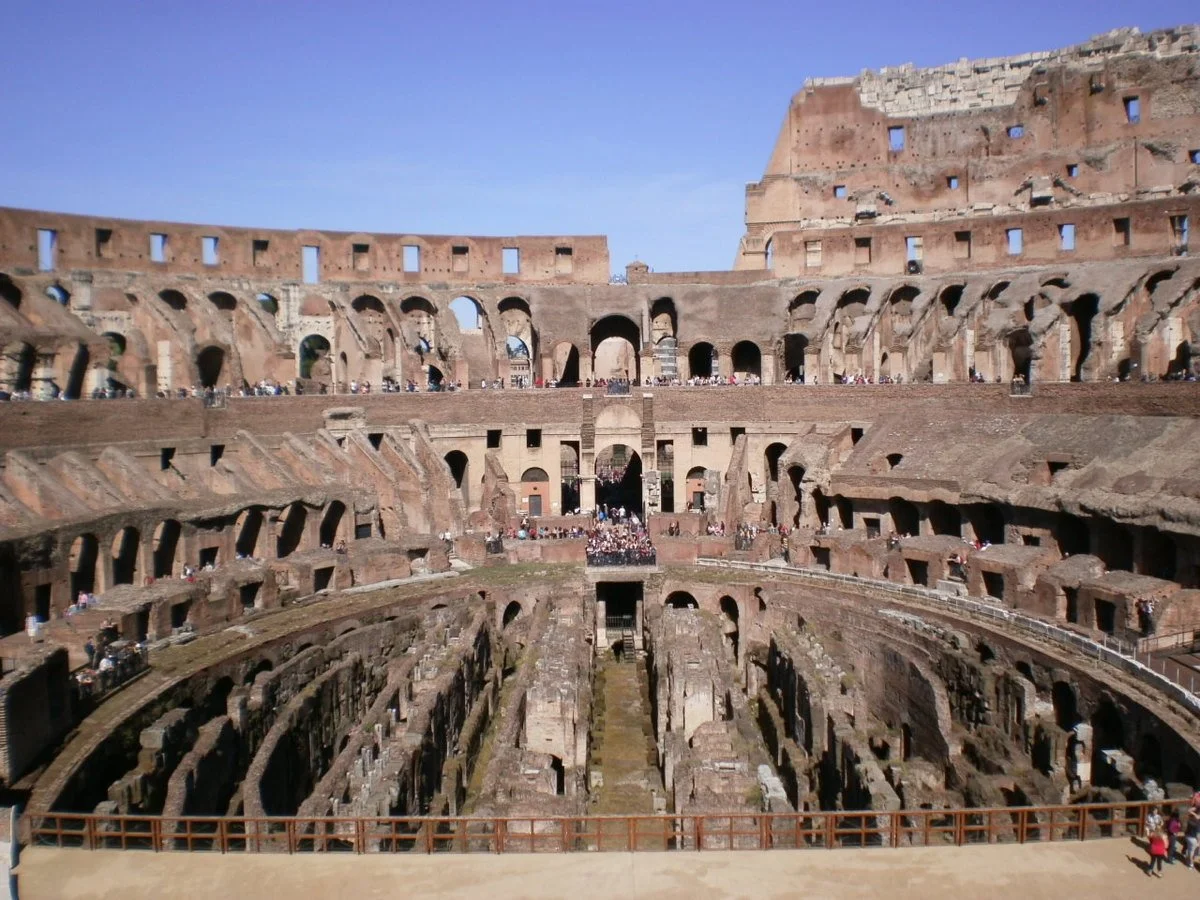
Game On: Exploring the Amphitheater
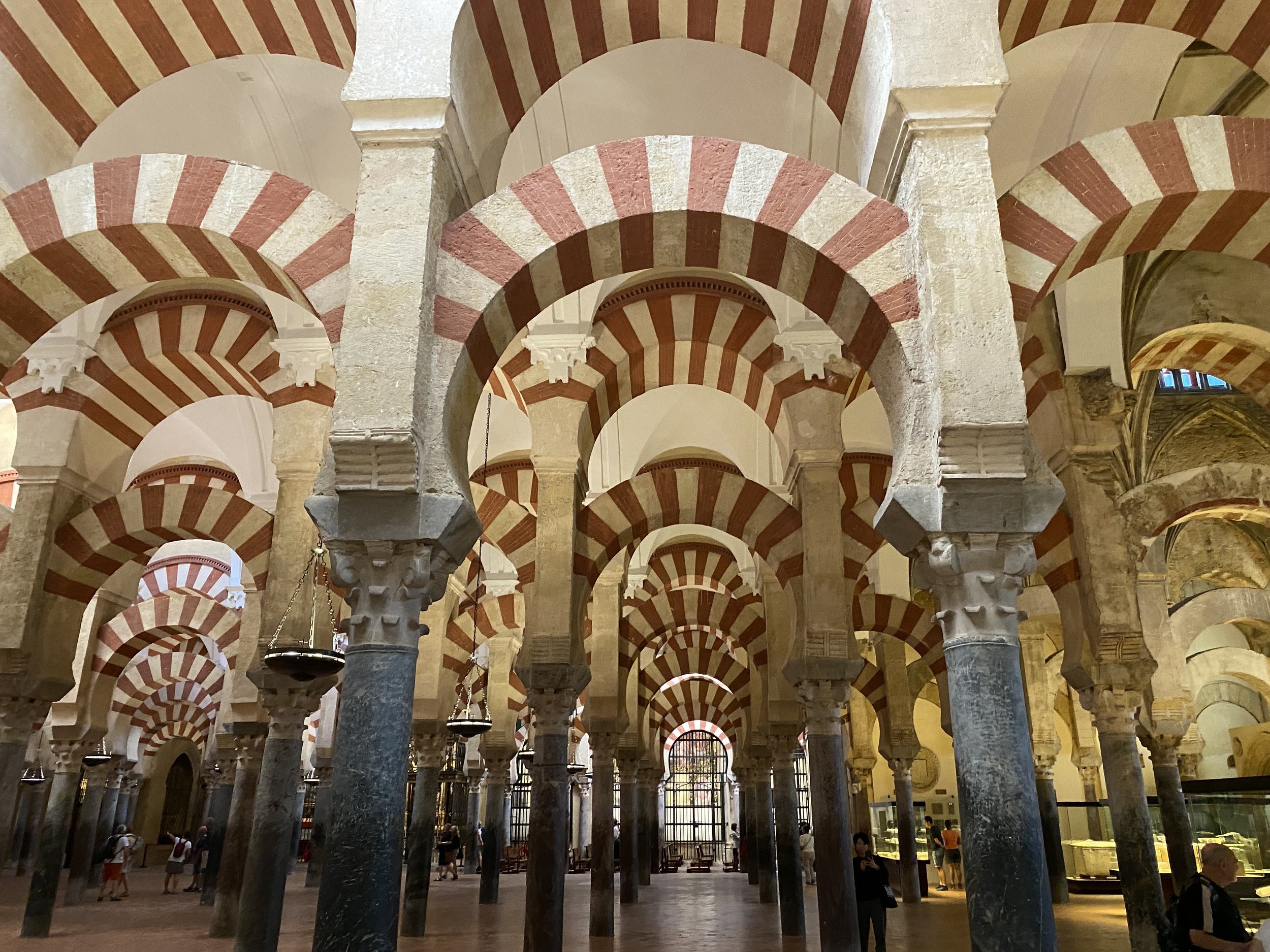
Situated just beyond the park’s entrance are the remains of the amphitheater. It was built between 117 and 138 CE and commissioned by Emperor Hadrian. When it was completed, it ranked among the largest in the Roman Empire and could accommodate up to 30,000 spectators — about half as many as the Colosseum in Rome, but far exceeding the scale required for a community of 8,000 inhabitants.
The interior portions are closed off to the public.
The site was used as a filming location and featured in the penultimate season of Game of Thrones. Thanks to some CGI-generated magic, it served as the Dragonpit, where three members of major houses have a historic meeting about a common enemy.
Attention, Game of Thrones fans! The amphitheater at Itálica, with some help from CGI, became the Dragonpit.
The amphitheater was the stage for the spectacle of bloodsport: gladiatorial combat, historic battle re-creations and animal hunts. Romans of all social classes attended, and the stand levels were carefully regulated and divided into a hierarchy based on wealth, gender and status. The lowest tier, or ima cavea, was closest to the action, reserved for the highest-ranking males. Women and the poor, meanwhile, sat or stood on wooden benches in the highest part of the stands, the suma cavea, which was covered by an awning to protect from the heat.
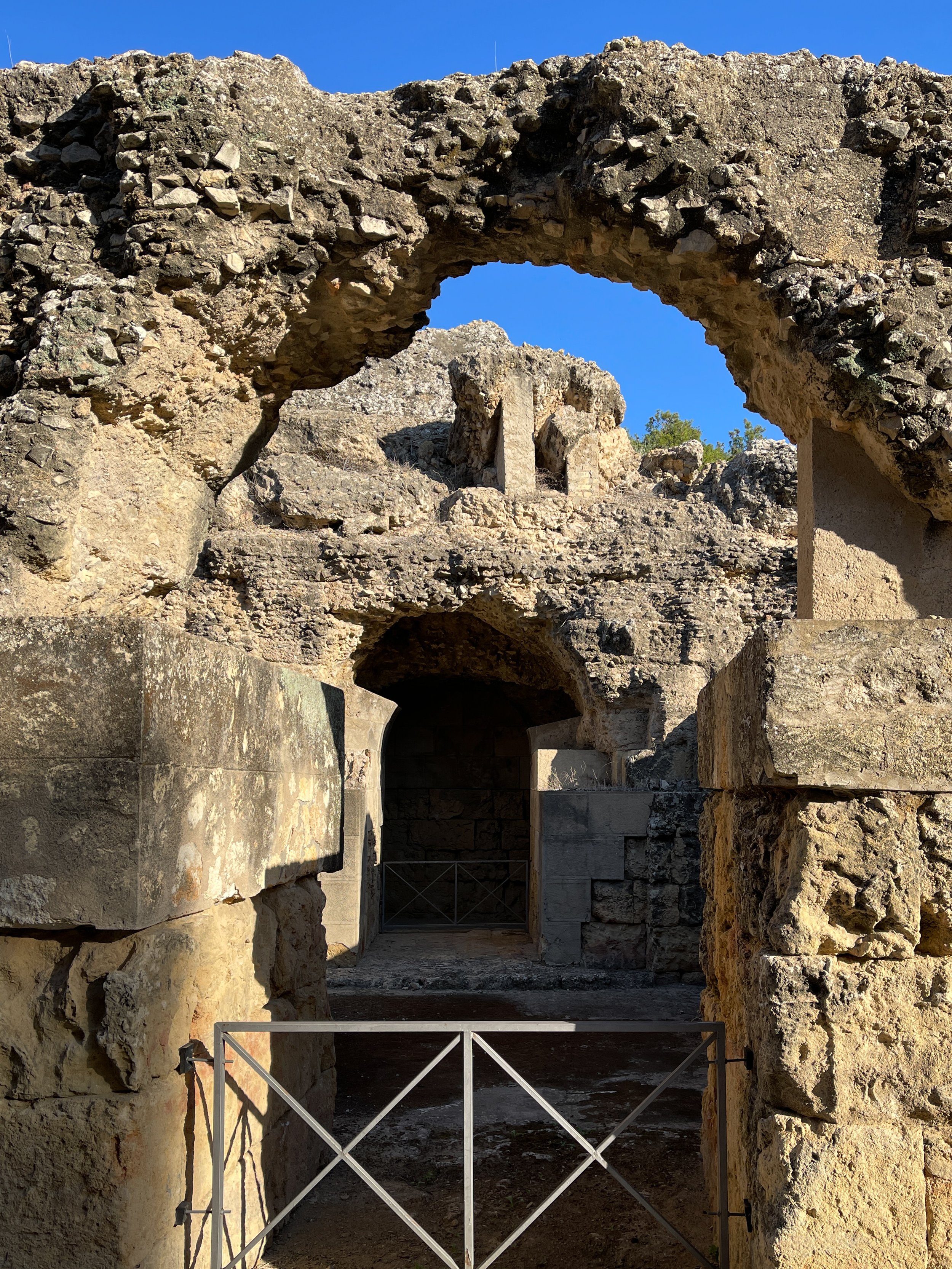
The passage leading to the fossa beastiaria, where wild animals were caged before being released into the amphitheater to be “hunted”
The massive rectangular pit at the center of the arena, known as the fossa beastiaria, was used to house the caged wild beasts that appeared in the spectacles prior to being released for the entertainment of the audience.
A variety of rather well-preserved murals can be seen at Itálica — though many of them are missing their central images.
Main Street Mosaics
We paused by a sign where the remnants of the city wall stood. In Roman times, the entire city was bounded by a walled perimeter. From here, you can glimpse the main sewer line, which runs through the Cardo Maximus (Latin for Main Street).
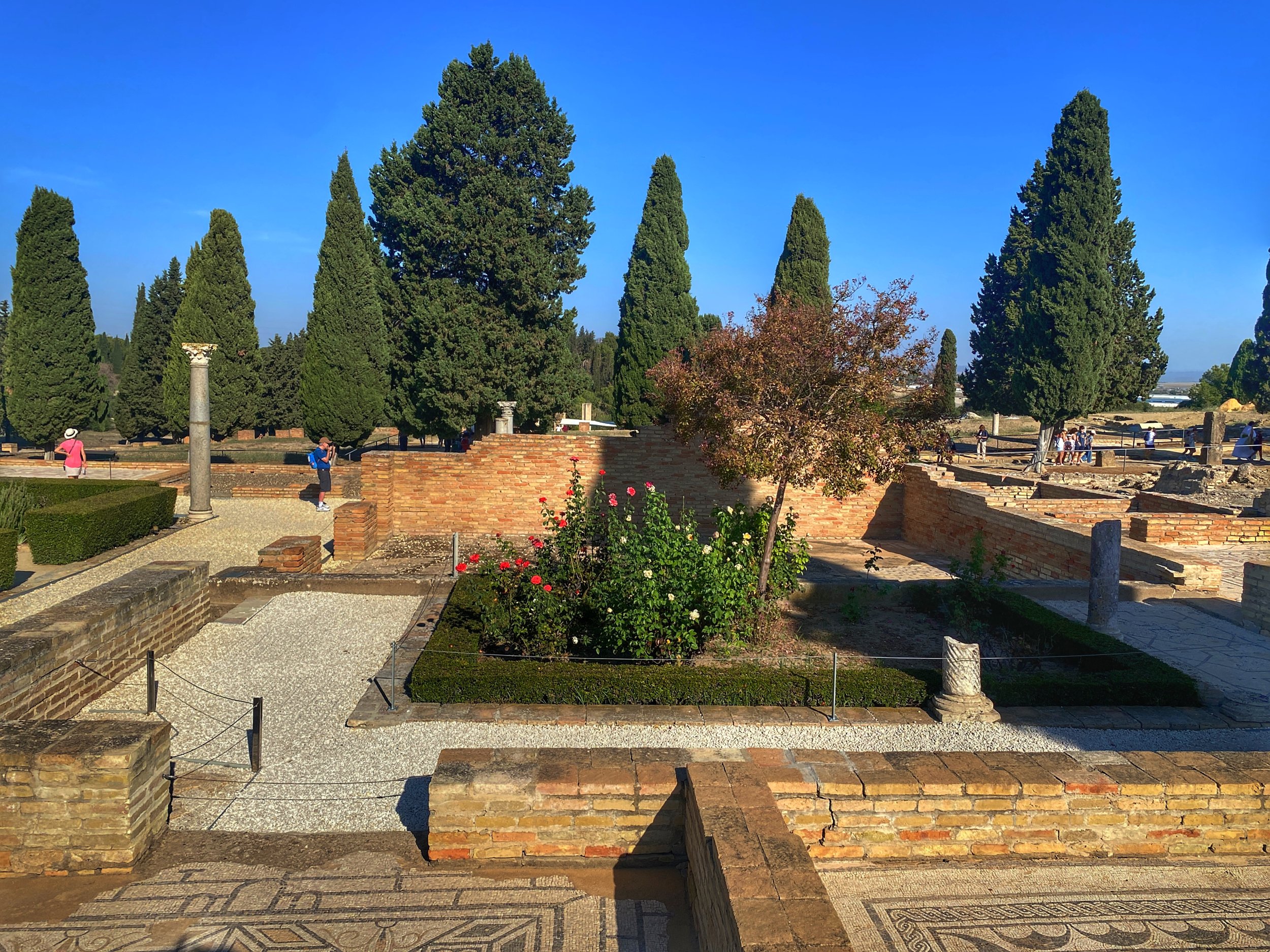
Beyond the amphitheater, large villas of prosperous families and municipal buildings have been excavated, many with colorful well-preserved mosaics.
The House of Exedra was a private club of sorts for the elite of Itálica.
Exedra, Exedra, Exedra
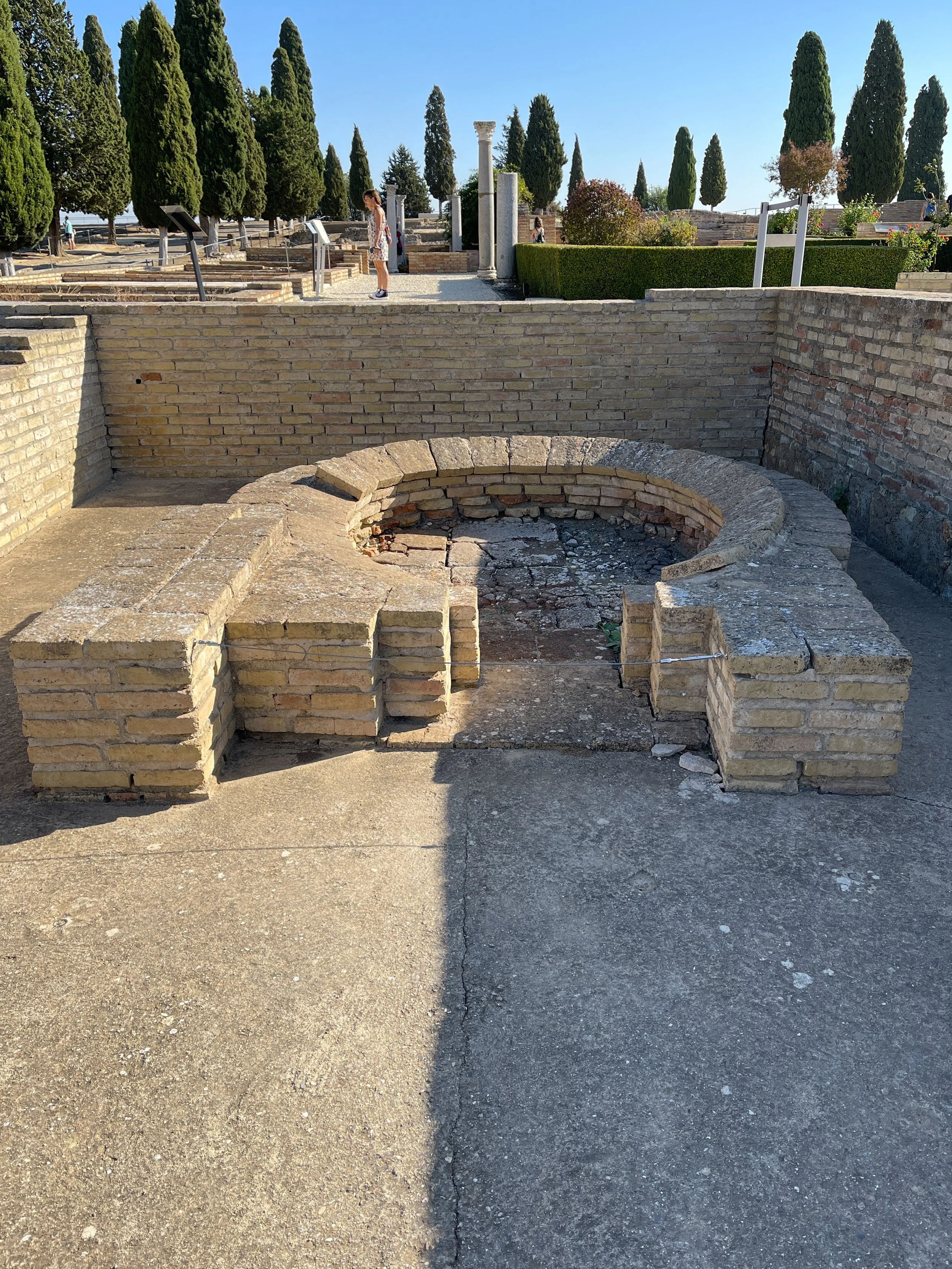
Spanning a surface area of 43,056 square feet (4,000 square meters), the Casa de la Exedra was one of the largest municipal buildings in Itálica. Due to its size and the inclusion of specific rooms, like the palestra (an open-air gymnasium) and latrine, historians have suggested that this structure probably served as a private club. Alongside the entrance were five tabernae, or shops.
At the heart of the complex is the peristyle, a garden courtyard featuring a curvilinear fountain. Adjacent to this was the exedra, a semicircular chamber with seating that served as a gathering place for upper-class citizens to engage in scholarly conversation. Originally, this area was covered by a high vault.
It also featured a thermae, which consisted of a series of rooms designed for bathing with hot, lukewarm and cold water — caldarium, tepidarium and frigidarium, respectively — as well as a changing room for patrons.
Potty humor? The floor mosaic of the latrine is embellished with scenes featuring well-endowed pygmies battling cranes.
As we walked along the perimeter of the structure, we stopped to take a look at the latrine. Although it’s been reduced to a shell, it still retains its marble bench with keyhole-shaped openings. The room was open, and the “toilets” had no partitions between them. When nature called, Romans had no issue hiking up their togas to conduct their business in close proximity to one another.
Look how close you had to sit to other people while taking a dump. Could someone pass the sponge stick, please?
The bench is positioned above a channel where a stream of water once pushed the waste into the underground sewage system. An attendant would provide patrons with a tersorium, a sea sponge affixed to a wooden stick, which was used instead of toilet paper to wipe their nether regions. These communal sponges were then rinsed in running water and submerged in a large pot filled with vinegar to sanitize them. Eww.
“At least they used vinegar,” Wally said.
The god Neptune, king of the sea, rules over a variety of mythological water creatures.
Go Fish: The Neptune Building
Although it hasn’t been completely excavated, the work carried out to date has indicated that one part of the Edificio de Neptuno functioned as a thermal bath, while another served as a municipal building.
Both structures cover an entire block, and the municipal building has intricate mosaics depicting Theseus and the Minotaur, along with a mosaic of Bacchus, the god of wine. The Theseus mosaic covers the floor of a grand hall and originally had a central panel portraying the divine hero within the Minotaur’s labyrinth. Meanwhile, the Bacchus mosaic features dancing maenads, satyrs, centaurs and tigers — figures typical of Bacchus’ entourage. Similar to the mosaic of Theseus, the depiction of Bacchus, the Greek Dionysus, is also missing.
At the time we visited, the mosaic was covered by netting for protection — but you can see a crocodile chasing a pygmy at the bottom.
The building that contained the bathhouse retains the remnants of its underground heating system. Within the frigidarium is the mosaic that gives the buildings its name. At its center is the sea god, wielding his trident atop a chariot pulled by two seahorses and surrounded by dolphins, fish molluscs and crustaceans. Its border includes scenes of fishing and combat with Egyptian iconography, depicting a hippopotamus, a palm tree, and the clearly popular but bizarre motif of pygmies battling cranes and crocodiles.
The remains of an oven from a bakery, one of the tabernae, or shops that lined the street-side of these luxurious villas.
Tabernae: Rome’s Retail Therapy
Tabernae could often be found along the perimeter of a household and served as an extra source of income for the owner of a villa. They included a variety of businesses, ranging from bakeries selling fresh loaves of bread to shops that produced small terracotta oil lamps called lucernes, and fullonicae, a kind of laundry or dry cleaner, where clothing was washed in a basin and agitated with a mixture of soda ash and urine. (Hey, apparently it worked.)
The main mosaic at the House of the Birds features various bird species, including a peacock, owl, rooster, pigeon, sparrow, heron, goose, parrot and mallard duck.
Pecking Order at the House of the Birds
The Casa de los Pájaros, also known as the House of the Birds, was the first domus, a private family residence, to be fully excavated in Itálica and likely belonged to an aristocratic family. Covering approximately 18,298 square feet (1,700 square meters), it’s divided into two primary spaces: a public area open to clients, tabernae and a semi-public area for those closely associated with the family; and a private area restricted to family members.
Kids on a field trip wander around the House of the Birds.
A room at the House of the Birds
A colorful, well-preserved mosaic
The semi-public area was arranged around a peristyle courtyard which would’ve been surrounded by a columned gallery. At the back of this courtyard, there was a niche known as a lararium that held small bronze figures dedicated to Lares and Penates, guardian deities that protected the household. The private rooms, including the triclinium (formal dining room) and cubicula (bedrooms) could be accessed from the courtyard.
The portion of the mosaic showing Hylas, Hercules’ well-endowed boy toy, getting sexually accosted by nymphs has been removed and is now in the Archaeological Museum of Seville.
Hylas, the Horse Hung Hero
Yet another elite residence in Itálica is the partially excavated Casa de Hylas, or House of Hylas. The northernmost courtyard connects to an anteroom, which served as a passage to the room housing the mosaic of Hylas, after which the house was named.
This mosaic portrays Hylas, the favored companion and lover of Hercules, being seduced and abducted by nymphs while collecting water from a spring. I’m certainly no prude, but the mosaic has a scene that made me clutch my pearls. One of the nymphs has her hand wrapped around Hylas’ calf while the other is clearly pulling his dick.
As mentioned earlier, this section of the mosaic has been removed and is now exhibited at the Archaeological Museum of Seville, leaving the surrounding geometric-patterned mosaic incomplete without its central image.
A mosaic at the House of the Planetarium depicts the Roman gods who were associated with each day of the week. In the bottom right, for example, is Helios, who drove the chariot that pulls the sun across the sky. Not surprisingly, he’s paired with Sunday.
Out of This World: House of the Planetarium
The last villa that Wally and I saw was the Casa del Planetario, or House of the Planetarium. The floor mosaic has seven medallions with depictions of each of the planetary deities who gave their names to the seven days of the week. This was Wally’s favorite, and he had to elbow some children out of the way to get a good look at it.
Centaurs and tigers line the mosaic of Bacchus and Ariadne.
The centermost celestial body of the mosaic is Venus, whose likeness is depicted wearing a jeweled crown and necklace, perhaps an allusion to the brightness of this star. As a divinity, she’s associated with Friday, the sixth day of the Roman week, and her prominent position suggests that love, one of her attributes, moves the universe.
Surrounding Venus are Helios (Sunday), Luna (Monday), Mars (Tuesday) Mercury (Wednesday), Jupiter (Thursday) and Saturn (Saturday).
The gladiator Wally celebrates yet another stunning win.
Tips for Itálica
We had an incredible time and spent about two and a half hours leisurely exploring the site. It exceeded my expectations. We were impressed by the sheer scale of the amphitheater and the quality of the mosaics. Except for a school field trip, complete with costumed chaperones dressed in Roman garb, the crowds were sparse, which made it feel like we had the place (somewhat) to ourselves. Plus, the majestic cypress trees dotting the landscape lend Itálica an atmospheric charm.
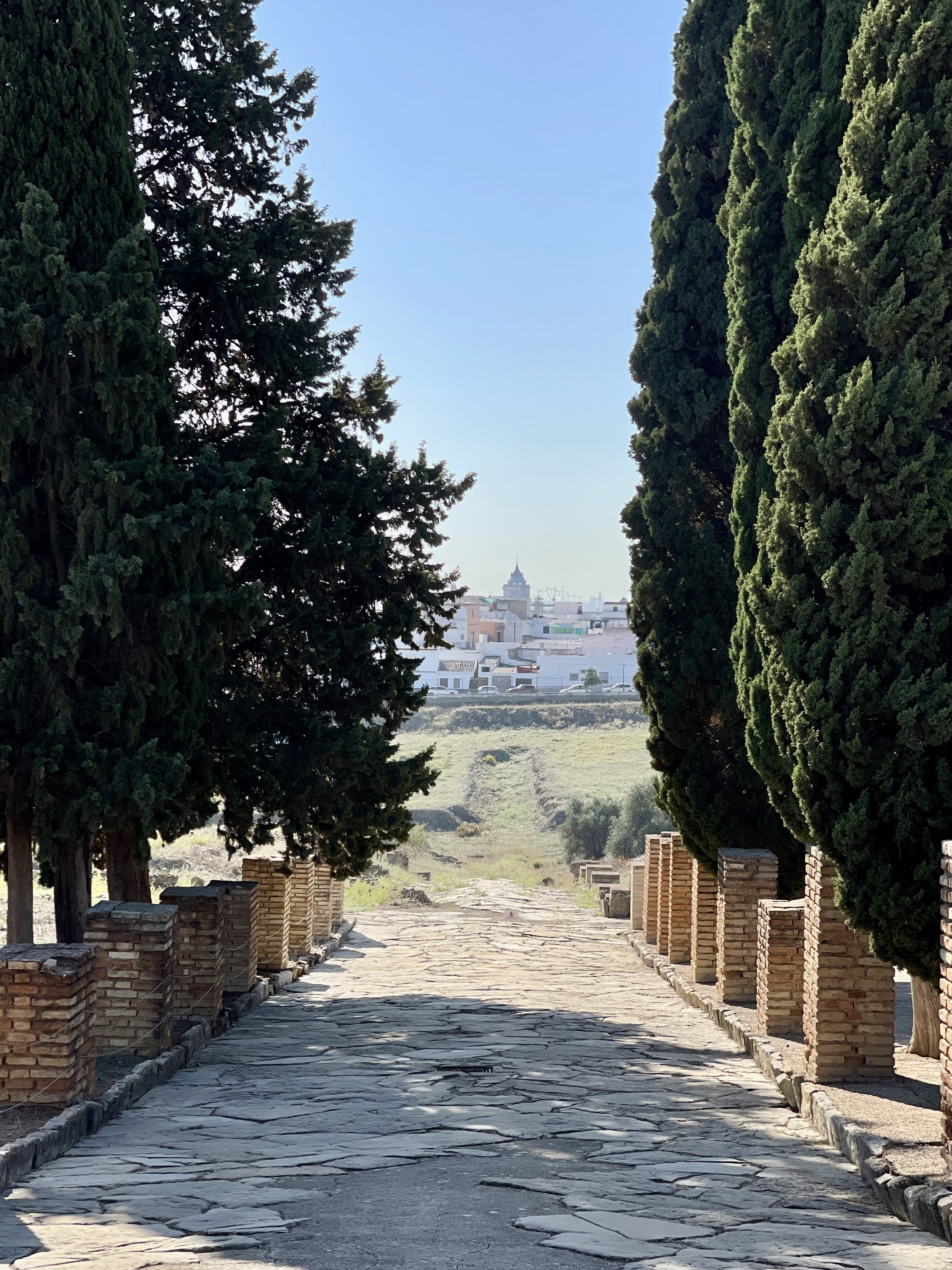
This elevated spot in Itálica offers a scenic view of the cobbled Roman road and the town of Santiponce.
On a practical note, remember to wear comfortable shoes for your visit and to bring sunscreen; there was little to no shade throughout the park. Also drink plenty of water. We brought two large bottles of water and snacks with us and were glad we did because there is no longer a café on the premises.
If you’re seeking a fun half-day trip close to Sevilla, I highly suggest hopping on the bus to Itálica. The archeological site’s ancient charms will be part of the mosaic of your memories. –Duke