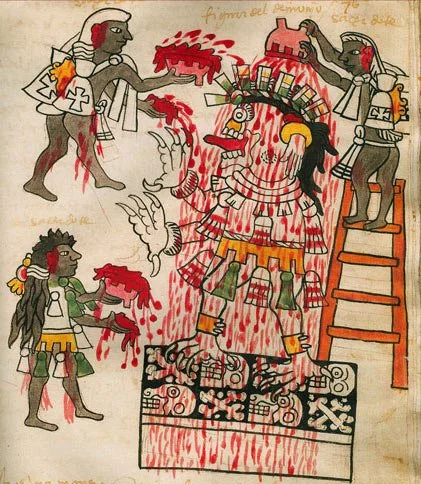
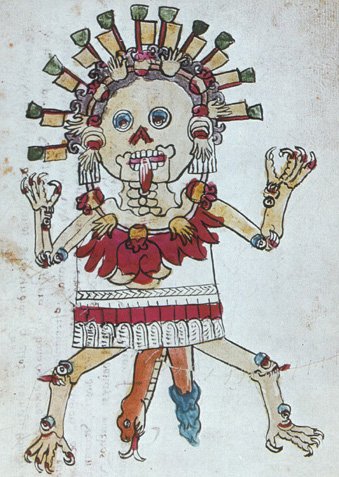
The Día de los Muertos ofrendas at the National Museum of Mexican Art focused on victims of COVID as well as gun violence, including the students and teachers killed in Uvalde.
Día de los Inocentes (Holy Innocents Day) by Claudia Álvarez, 2010. The sculpture represents the story in the New Testament where King Herod orders the massacre of all children under the age of 2 in an attempt to kill the baby Jesus.
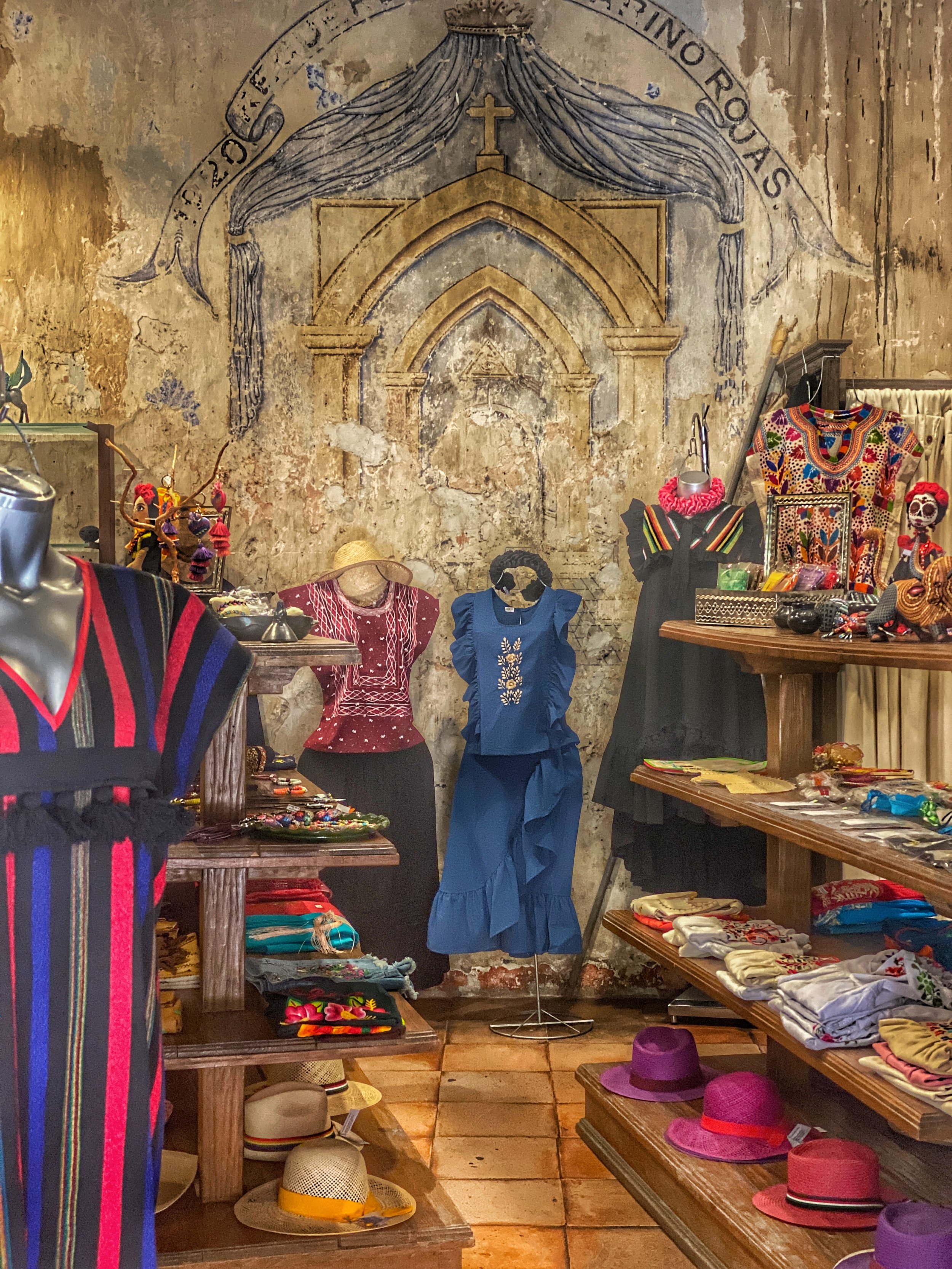
The Mexican tradition of honoring loved ones with an ofrenda is something every family should adopt. These homemade altars are typically adorned with marigolds, photos, and items the deceased person would appreciate, including their favorite foods and beverages (empanadas and a margarita on mine, por favor). But even if you don’t create one at home, you can see artistic interpretations if you’re in Chicago.
Sometime around mid-October, Duke and I head to the Pilsen neighborhood to see the Day of the Dead ofrendas at the National Museum of Mexican Art.
The original concept of the exhibit was to honor people in the USA who had been murdered.
“In the last decade, we have been overwhelmed with the amount of mass shootings on an annual basis that there have been far too many for this exhibition,” reads the sign at the start of the exhibit, proclaiming, “Enough is enough!”
This year, the 36th Day of the Dead installation, covers not only senseless gun violence — including a moving memorial to the victims of the Uvalde school massacre — but Mexican actors who passed away and those lost to COVID and suicide.
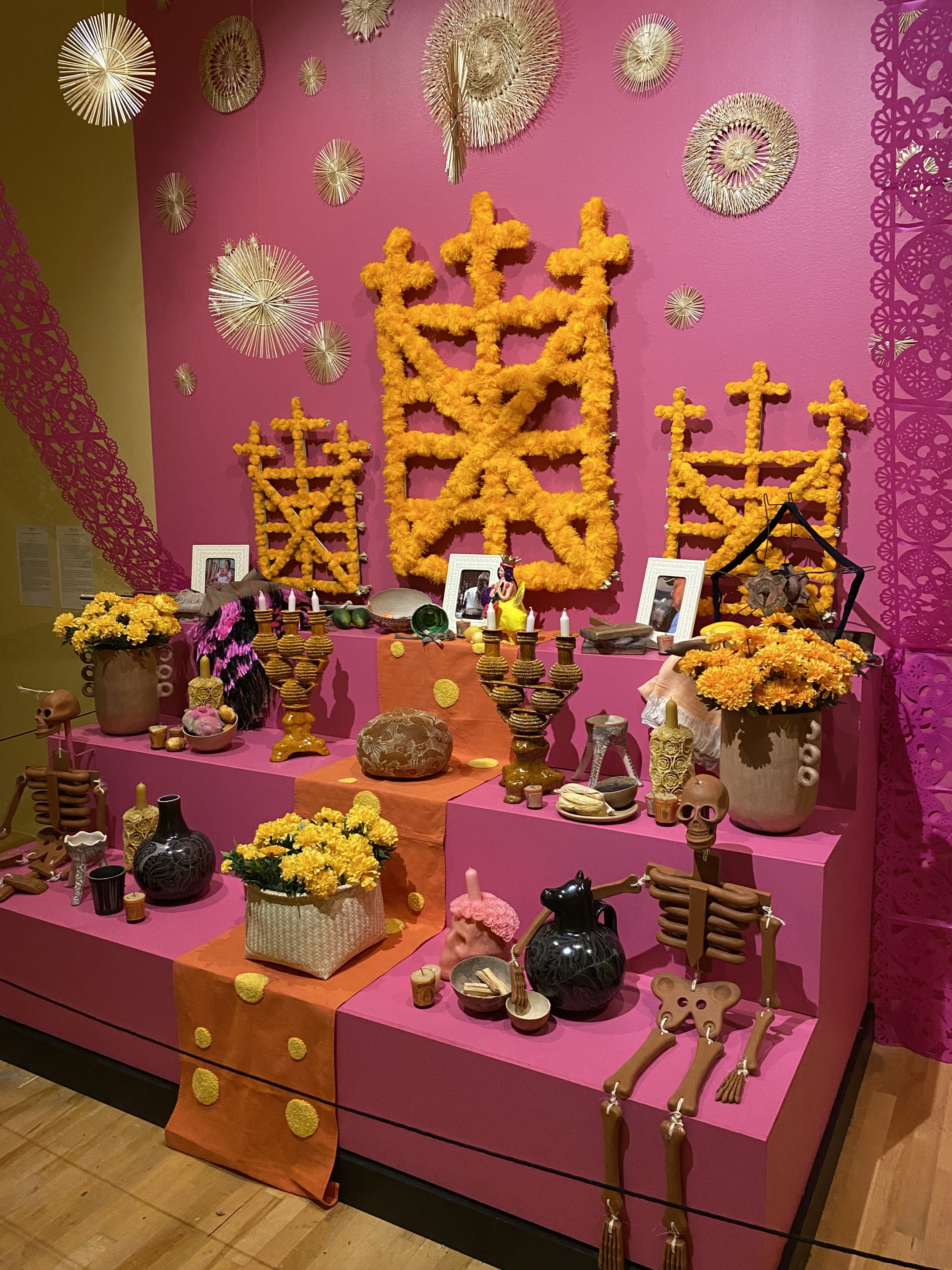
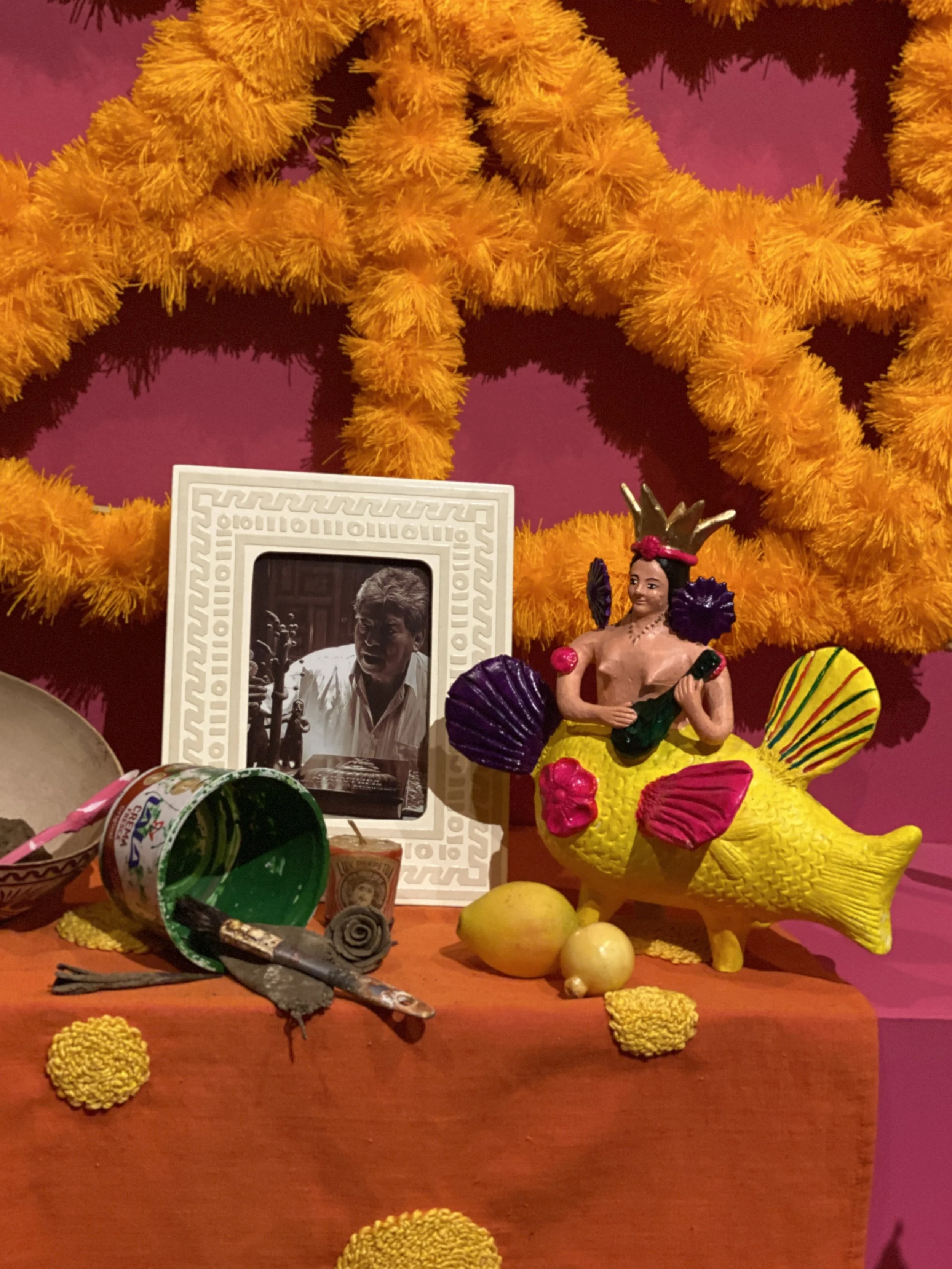
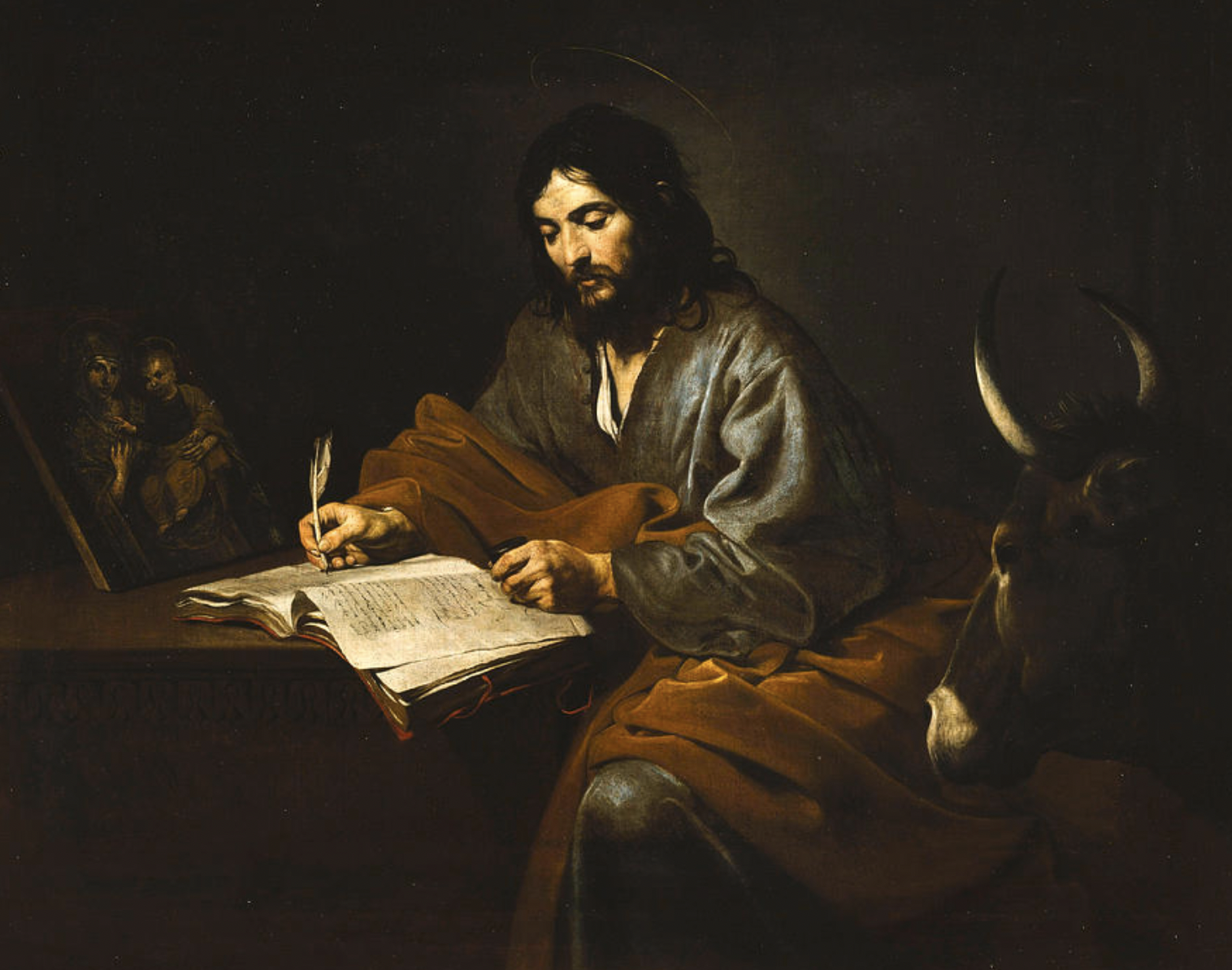
Ofrenda to artisans who died of COVID
A photo of one of the artists memorialized in the ofrenda, Tiburcio Soteno Fernandez, with the tools of his trade and his iconic mermaid alebrije.
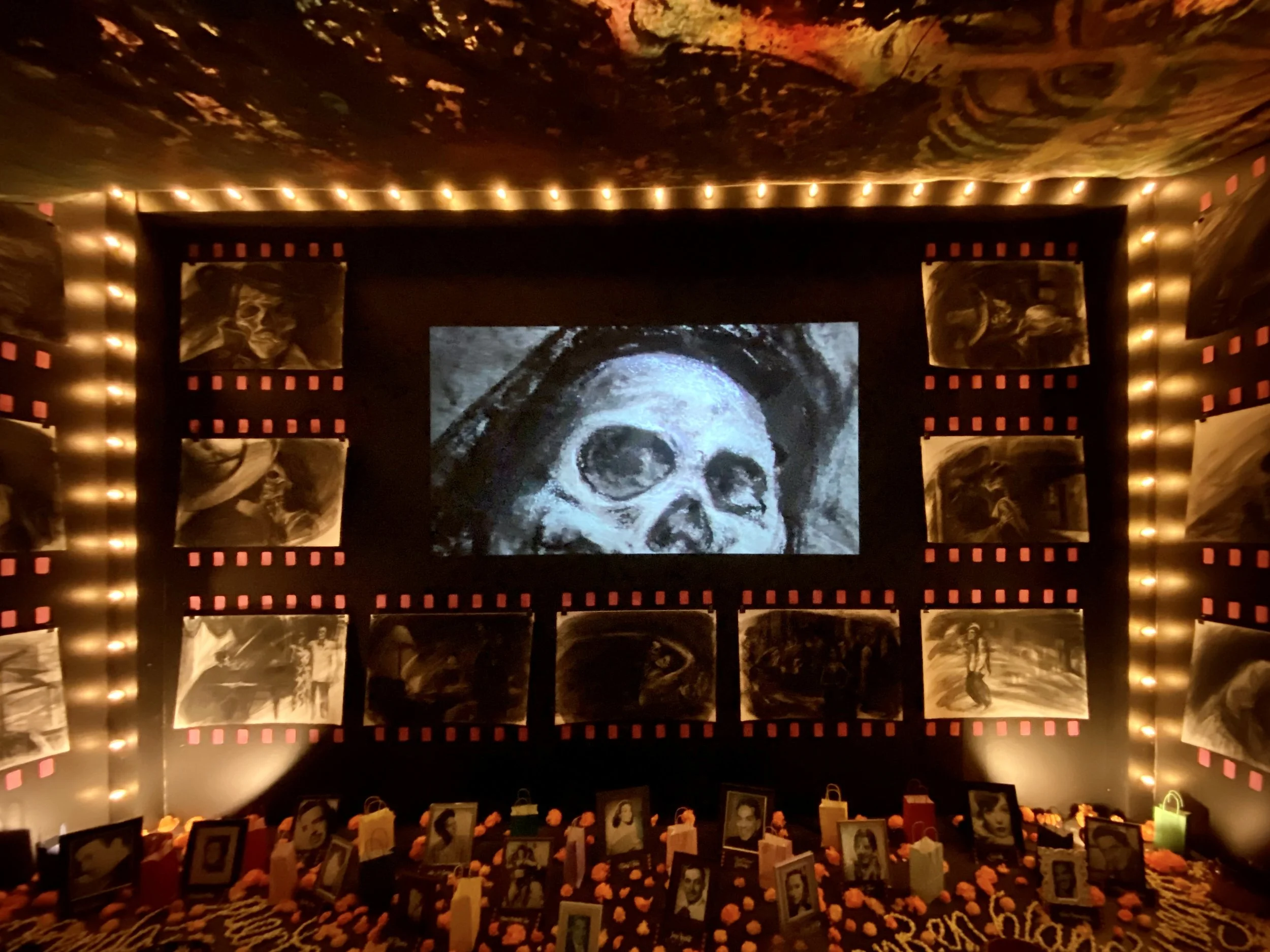
An ofrenda to Mexican cinema by the Puerto Rican Antonio Martorell
La muerte allá donde la vida no vale nada (Death, Where Life Has No Worth) by Alejandro Cortés, Dolores Gómez Navarro and Jorje Negrete. Note the upside-down ofrenda, pointing to Mictlan, the underworld of the ancient Mesoamerican peoples.
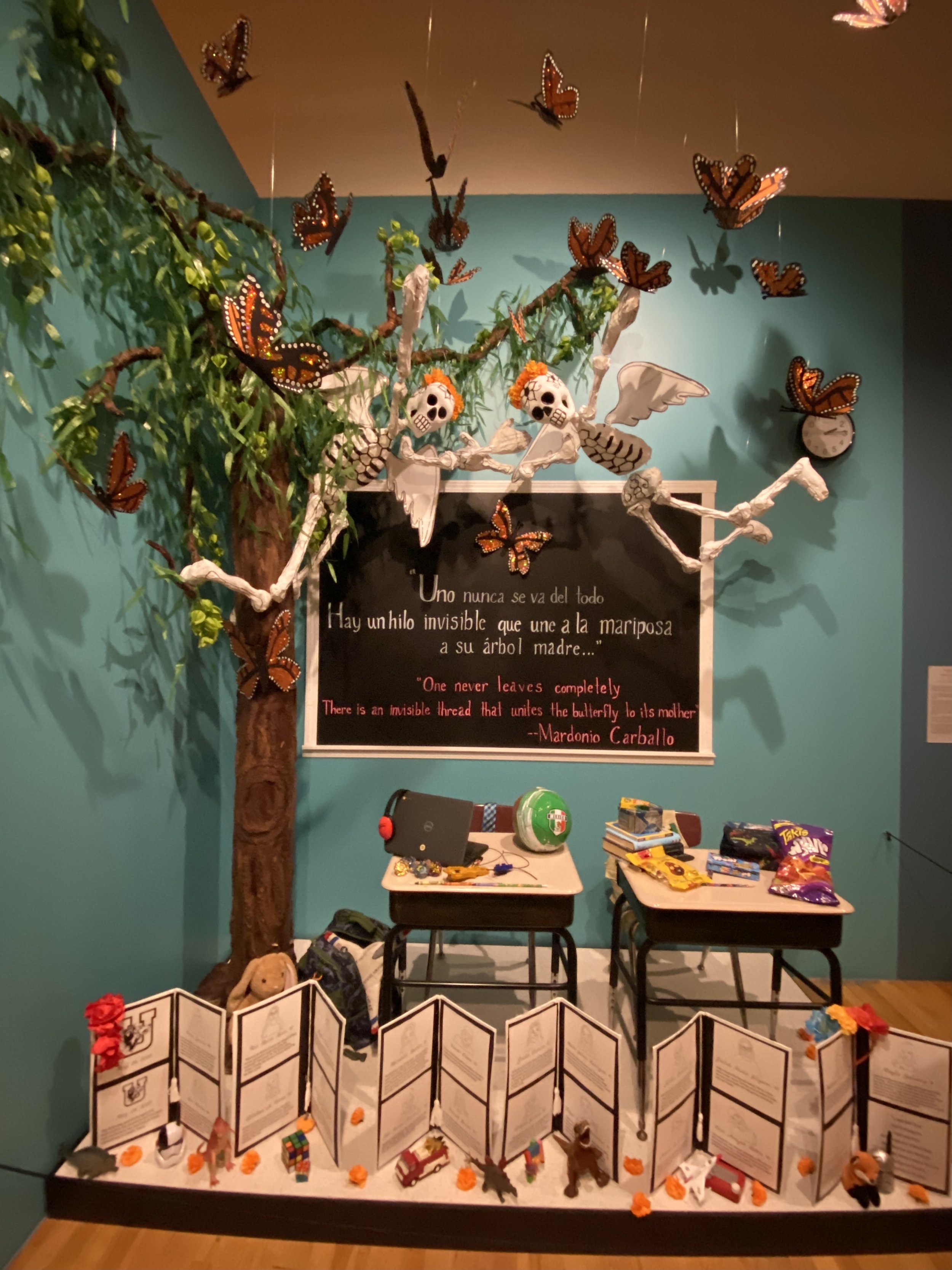
An ofrenda to the Latinx victims of the Uvalde, Texas shooting at Robb Elementary School. It was created by students at Bernard Moos Elementary School in Chicago.
Ofrenda a los Arrancados (Ofrenda to the Uprooted) by Carlos Flores. He used “bandit signs” to pay tribute to the working-class people of color who disproportionally lost their lives to COVID.
This ofrenda, created by the Ukrainian Institute of Modern Art, pays homage to weavers of the war-torn country.
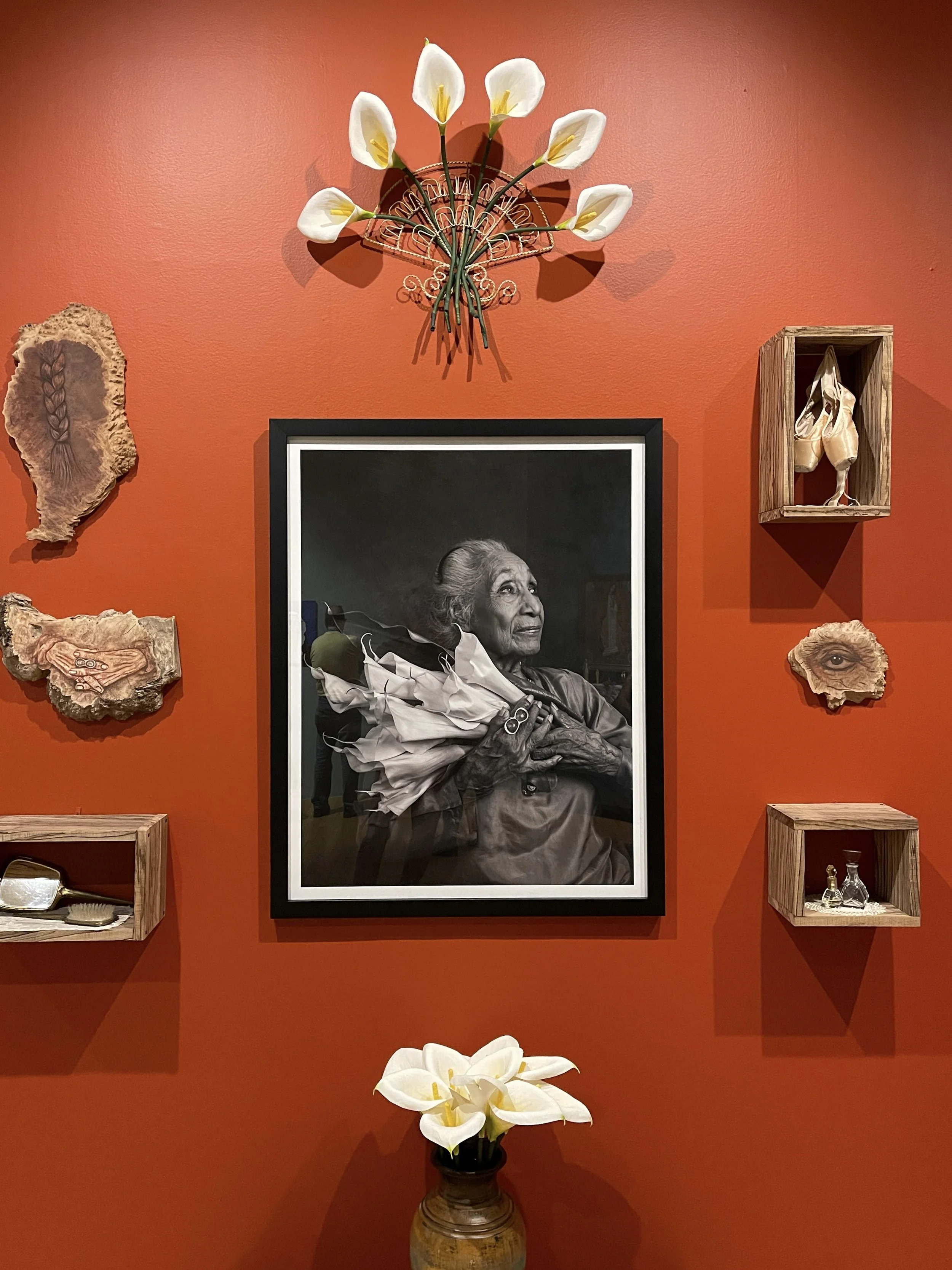
Ofrenda to Nieves Orozco Field, an indigenous dancer who modeled for Diego Rivera
Molds used to make sugar skulls for Day of the Dead
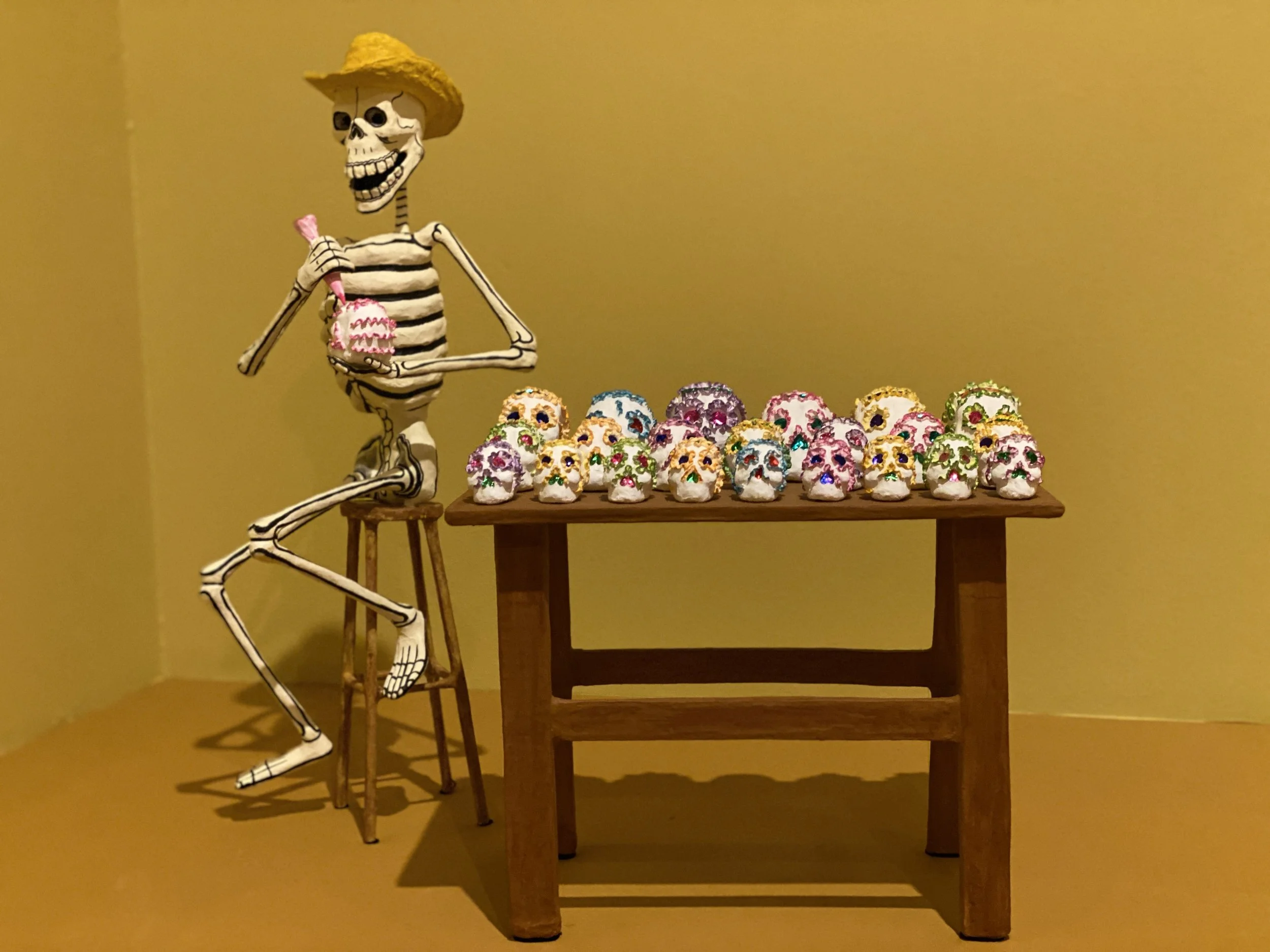
Skeletons go hand in hand with Day of the Dead, as do sugar skulls.
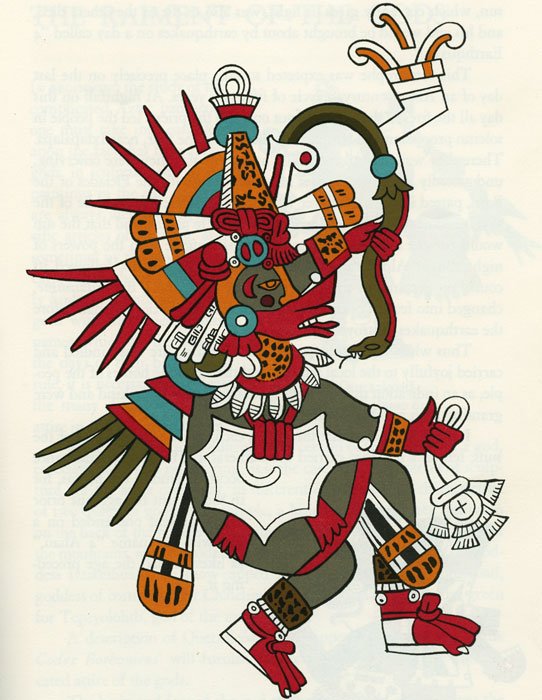
Año de los Muertos (Year of the Dead) by Eric Romero, 2020
A Tree of Life with Mexican rites and rituals by Israel Soteno, 2007
If you’re in Chicago in the fall, you should definitely stop into the National Museum of Mexican Art (it’s free!) to see their ofrendas. ¡Feliz Día de los Muertos! –Wally