Were coyotes introduced to get rid of the raccoons? And just how dangerous are the coyotes in Chicago?
They’re cute — and a bit frightening. But the coyotes in Graceland Cemetery in Chicago haven’t hurt anyone and keep to themselves. Photo by Adam Selzer
I never can resist a stroll through a graveyard. One winter day, I walked past the entrance of Graceland Cemetery at the intersection of Clark and Irving Park in Chicago. Before I even knew what I was doing, I found myself heading through the iron gates.
The cemetery is enormous and full of gorgeous old graves and mausoleums, some of which house the remains of famous Chicagoans, including the architect Louis Sullivan and the department store magnate Marshall Field.
Wally thinks this might have been the copse where the coyote made her den.
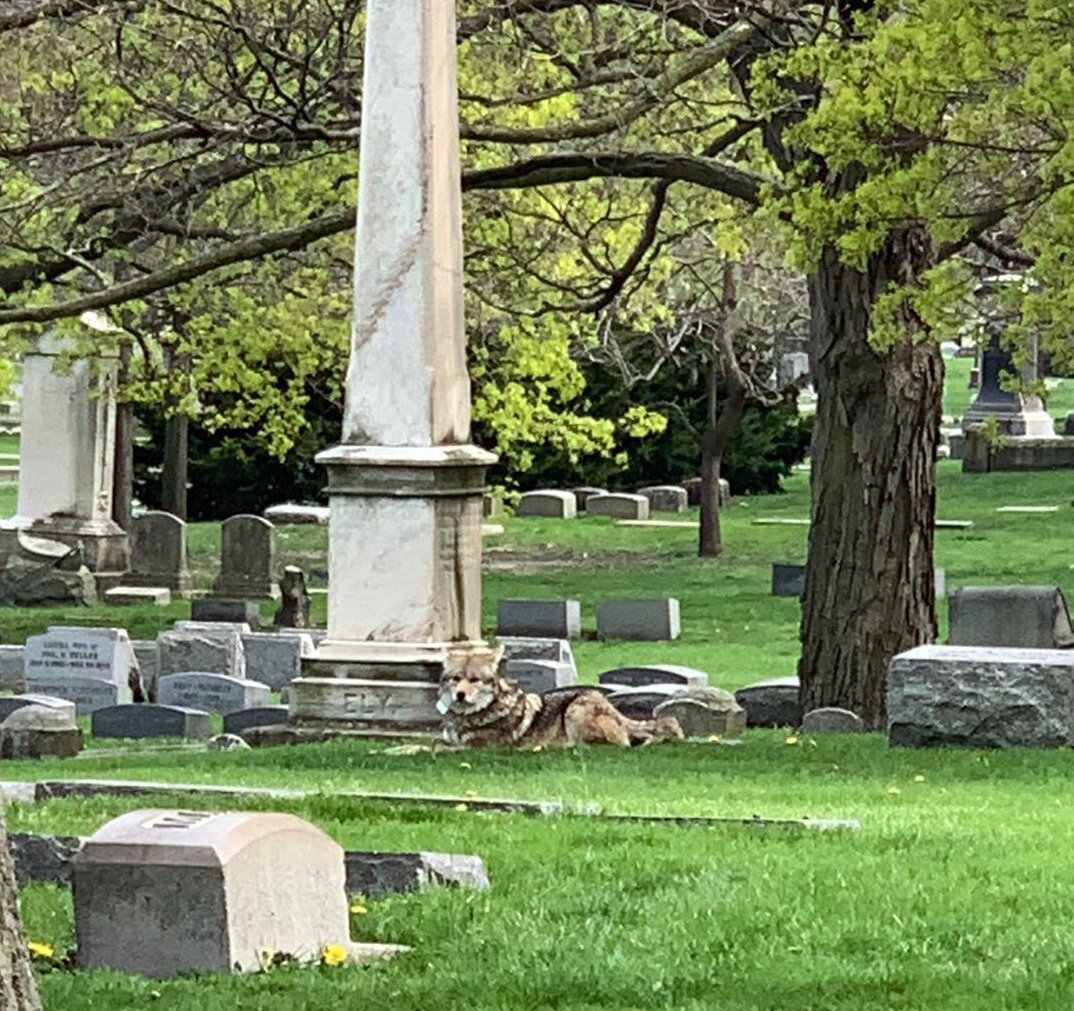
As I wandered around the pond at the northern end of the cemetery, I noticed movement out of the corner of my eye. A dark shape emerged from a cluster of brambles about 20 feet away, its brown fur in stark contrast to the whiteness of the snow-covered ground. The creature stared at me, then crouched a bit, its ears flattening, and slowly began to prowl in my direction. I realized this must be a coyote — people in Chicago talk about these creatures roaming the streets at night — and despite its inherent cuteness, I had no doubt it could inflict some serious damage.
I was carrying a tote bag with my laptop inside, which I now desperately clutched like a weapon, ready to swing it at the beast if it decided to attack me. I backed away, slowly at first, so I could keep the coyote within my sights. Once I had gained some distance, I started running through the snow, finding one of the roads that led to the main entrance.
Can you spot the coyote? These wild canines help curb populations of raccoons, rats and geese at Graceland Cemetery. Photo by Adam Selzer
Out of breath and slightly traumatized, I darted into the cemetery office near the front gate. A young man smiled at me as I shouted, “There’s a coyote in the cemetery!”
“Oh, yes,” he said calmly. “There’s more than one.”
I blinked at him, dumbfounded. I mean, I understand why cities would allow squirrels and bunnies and even deer to roam our green spaces — but why would it be OK to have large wild dogs running free? As insane as it sounds, there could be up to 4,000 coyotes in Chicago, according to NPR.
“In fact,” the young man continued, “the city brought the coyotes into the cemetery to eradicate the raccoon problem.”
This was getting stranger and stranger. It seemed to me that, in this case, the solution might be worse than the problem.
“I might have been imagining things,” I said, “but it seemed as if it was pursuing me, like it might attack.”
He nodded. “There’s never been an attack in the cemetery, but she just had a litter and was protecting them.”
That being the case, it sure would have been nice to have a warning posted, something along the lines of: Caution! Keep a lookout for a mother coyote that could maul you because she feels you’re a threat to her babies. Enjoy your visit!
As strange as it might seem, it turns out coyotes are indeed fixtures within Chicago city limits and are, in the vast majority of cases, not a threat to our safety. There are, of course, exceptions to this rule, such as the 6-year-old boy who was bitten by a coyote near the Nature Museum — though who knows? The kid might have done something to instigate the attack.
There are typically three to five coyotes within the grounds of Graceland Cemetery. Photo by Adam Selzer
The Official Word on Coyotes at Graceland
Wanting to get to the bottom of this mystery, I reached out to Graceland’s staff to ask them about coyotes in the cemetery.
No one is sure of exactly how many coyotes are on the grounds, but employees estimate there are usually about three to five.
“The coyotes have never hurt anyone on the grounds and stay away from people,” says Jensen Allen, associate director at Graceland. “We do not allow people to feed them, which is usually what can cause animals to become accustomed to up-close human interactions.”
Did the city really introduce them to the cemetery to deal with the raccoon population?
“We cannot verify whether they were brought into the city for any reason or not,” Allen says. “There are many stories out there, but we have heard from wildlife experts that this is not true per se. Coyotes have been part of the city for an extremely long time, and it is likely humans encroached upon their territories long ago and they have become used to surviving in urban areas.”
Either way, raccoons are more of an issue to people than the coyotes have ever been, she attests. “As I’m sure you know, raccoons are pretty fearless and will approach humans with no issue. We are thankful to our coyotes because they keep raccoons down as well as other vermin such as rats, mice, geese and any other troublesome wildlife animal.”
Our friend Sandy and her daughters visit Graceland often — and are always excited to see a coyote.
To learn more about coyotes (and be tempted to hold one of their cute little puppies — even though this is a very bad idea), check out the Urban Coyote Research Project. –Wally
Graceland Cemetery
4001 N. Clark St.
Chicago, IL 60613